Example Quarter wave plate thickness calculator #2: INPUTS: Wavelength = 590 nm, n0 = 1.66, ne = 1.49 OUTPUTS: Thickness = 867.65. Quarter wave plate thickness formula or equation. Following quarter wave plate thickness formula is used for this calculator#2. Refer difference between half wave plate vs quarter wave plate. Bass Reflex Box Calculator Onken Bass Reflex Calculator Calculate Speed of Sound in fibrous material Calculate the Required Amplifier Output Power Calculate Back Loaded Exponential Horn Calculate Tapered Quarter - Wave Tube Calculate Baffle Diffraction Loss.
Back to home page
Back to audio main page
Back to loudspeakers main page
Overview: This is a calculator for designing a Dual Chambered Tri-Tuned Bass Reflex Enclosure. The formulas used in the calculator create a design that suggests the most maximally flat response in an anechoic environment based on the number of drivers, the thiele small parameters and the allotted dimensions specified in the user’s input fields. TheContinue reading →.
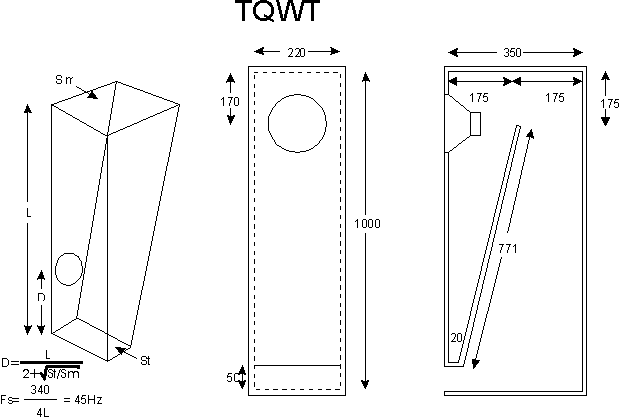
First described by Paul Voigt in 1930, TQWTs allow a good quality-to-price ratio. They are also easy to build.
Similar to transmission lines, the TQWT is different by its shape, a kind of horn is used as back load but the driver is not placed at the beginning of the cone as usual but on its side.
The port is used to adjust the rear flow according to the driver type, internal damping and desired response.
The resonance frequency depends only on the length L of the cone and the driver position is calculated by the formula indicated on the schematic.
During the tune-up, it's a good idea not to close definetely a side of the box to allow an easy modification of the internal damping.
The height of the port should also be adjusted through both measurements and listening sessions.
It's not advisable to select a very low frequency cutoff as a not very refined bass could be obtained.
The TQWT adapts very well to full-band drivers or bass-medium drivers of small dimensions.
The folded horn gives a very practical loudspeaker with a driver positioned at the right height without any support.
Example 1
Example for a 170mm driver. The lower cut-off is at 45Hz. May be enhanced with a tweeter and a simple passive crossover.
Example 2
Razorsql serial key. Here is another version for smaller loudspeakers:


Example 3
Example using a 130mm driver like the Fostex FE127 but could use also smaller 100mm drivers like the Fostex FE103 or FE103 Sigma.
Example 4
By Gérard Chrétien, published in L'Audiophile # 38 (Spring 86).
It uses a Triangle T17FL (170mm) as woofer-medium and a tweeter Technics 5HH10.
As the T17FL is no longer available, you can replace it by a Triangle TP16PP122o (Fs=53Hz, 92dB).
The tweeter can be replaced by the Triangle TZ20 (93dB) with probably no resistive network.
Schematic
Filter
Ground Plane Calculator
This very simple filter operates at 8KHz/6dB and the level of the tweeter is reduced by around 5dB to match the woofer.
Damping
A big work was done to obtain the best damping.
Loop Antenna Calculator
During the damping tuning a side is not definetely closed.
Ground Plane Antenna Calculator
Other Photos
The loudspeaker (nearly) finished.
Back to top